by Ana Moreno Salvo

New Pedagogies for Deep Learning (NPDL) is a global innovation partnership committed to transforming learning so that all learners thrive by developing the six global competencies – citizenship, character, communication, critical thinking, collaboration and creativity – they need to flourish in this complex and ever-changing world. Deep Learning includes a set of collaborative learning tools and processes that transform teachers into activators and architects of learning.
Interview with Joanne Quinn
Deep Learning enables educational innovation on a global scale in tune with the needs of the twenty-first century and educating the world. Could you explain why you chose ‘Engage the World – Change the World’ and how you talk about the project?
We began the Deep Learning work ‘to foster deep learning so that ALL learners contribute to the common good, address global challenges and flourish in a complex world’.
The hyper-connectedness of today’s world means that in addition to internal development, young people also have to possess the skills to collaborate and problem-solve with others from a wide range of cultures and backgrounds.
We need to make learning as addictive as social media, which means real-time interaction and the ability to see results. ‘Engage the World – Change the World’ thus embodies the philosophy that students learn for today and don’t have to wait to use that learning in the distant future.
In Deep Learning students learn for today and don’t wait to use that learning in the distant future

The six educational objectives of Deep Learning are prioritise education in being for learners. Could you explain to us why you chose them and especially why you consider character important, which few other systems do?
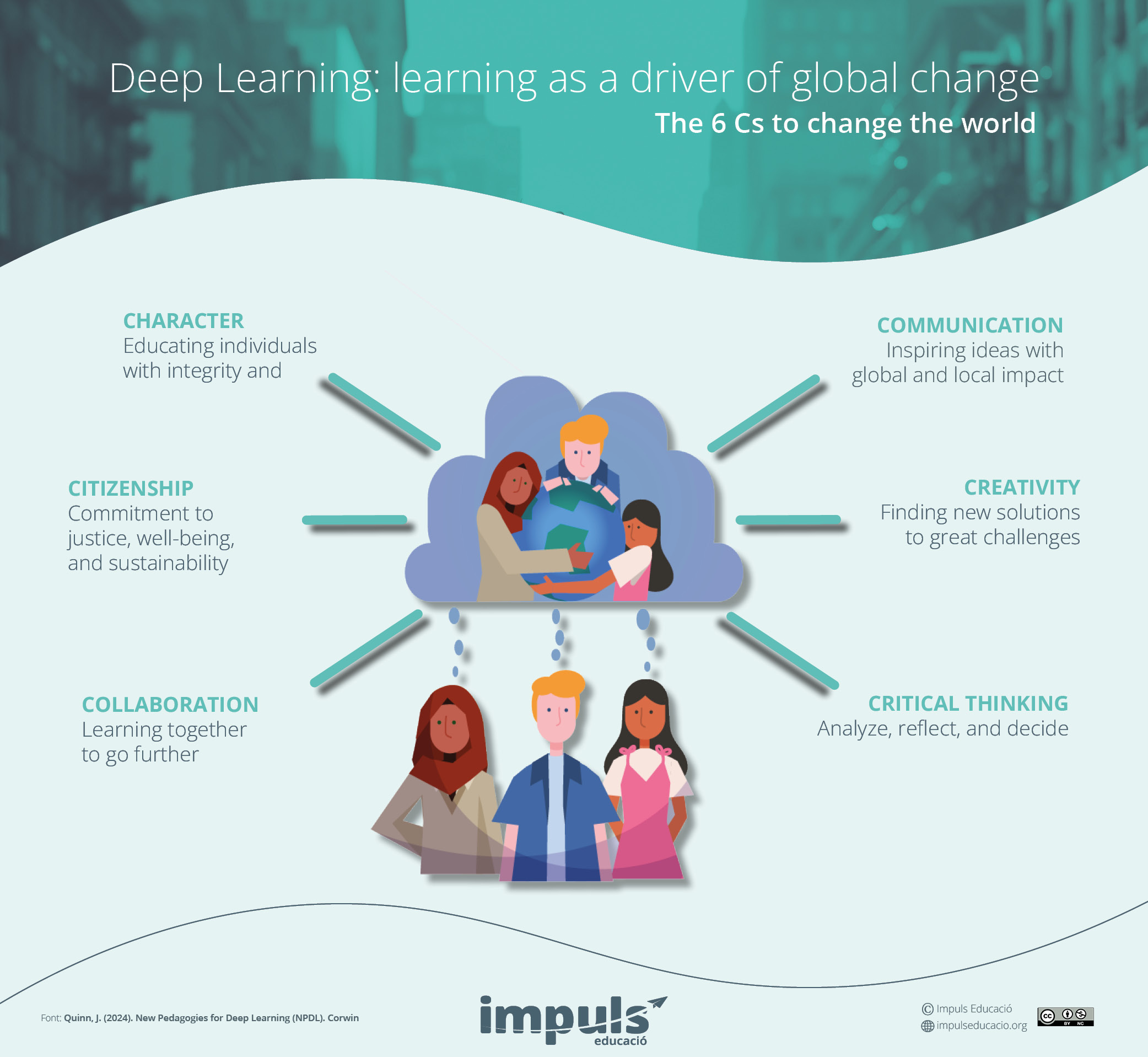
Deep Learning is now a global association in more than twenty countries. We started with a simple question: ‘What do we want students to know, to be able to do and to be?’. The words might vary, but when the groups reached consensus, six competencies emerged: Character, Citizenship, Collaboration, Communication, Creativity and Critical Thinking. Each of the six competencies has a set of specific dimensions that describe the key aspects of each and the way to develop it.
The terms Character and Citizenship were complicated because they have different meanings depending on context and culture.
As partners of Global, we chose the word ‘Character’ to describe three fundamental internal dimensions or attributes:
- Developing the social and emotional traits to be a lifelong learner capable of self-direction.
- Possessing tenacity, perseverance and resilience.
- Being capable of demonstrating empathy, compassion and integrity in action.
Citizenship in our model refers to the external demonstration of character and has three fundamental dimensions:
- Global perspective.
- Commitment to human equity and well-being through empathy and compassion for diverse values and worldviews.
- Genuine interest in human and environmental sustainability.
One idea is that character has been readily assumed and serves as a catalyst for the other five.
Figure 1. Deep Learning: Learning as a driver of global change
The goal is to change the world through education with the cooperation of different countries in ‘New Pedagogies for Deep Learning’. Why seek cultural change and not settle for a programme? How does it affect the students involved, their schools, teachers or communities?
The answer is simple: programmes come and go at the whim of leaders, budgets, politics and trends. Based on our work in the field of large-scale change, we know that positive, deep change has to be rooted in a strong culture of learning.
Innovations are living, evolving entities. They need clarity of purpose, objectives and a strategy to mobilise people, but they have to be able to adjust and pivot in this rapidly changing world.

We know that positive and profound change have to be rooted in a strong learning culture
Deep Learning was conceived as a new mindset that encompasses everything we know about organisational learning and change. Our framework for deep learning is as simple as it is necessary to cut across contexts and countries, but it has to be comprehensive. It includes the six competencies needed by everyone (learners and adults) and four elements of learning design that support the development of deep learning experiences.
At Deep Learning, you achieve excellence and equity. What are the keys to making this happen?
Our approach is asset, not deficit-based, and based on learners’ needs and interests. To support this goal, we design learning using four elements or decision points. Two elements that have a major impact on both learning and equity are learning partnerships and learning environaments.
Learning partnerships focus on relationships: student-to-student, student-to-teacher and everyone-to-community. The second element that impacts equity is the learning environments, which address the learning culture established. Human beings need to feel safe and sense that they are valued and belong to a group in order to learn effectively. These are the same factors that contribute to well-being.
Being explicit about a culture that honours students’ gifts increases their confidence, engagement and achievement

Respectful relationships and a culture of belonging create learning that is authentic and intrinsically more engaging. This combination of strategies, learning partnerships and learning environments creates an environment focused on success rather than deficits. This mutual reinforcement is what is helping to move the needle on equity and well-being.
How do you create a Deep Learning environment that prepares students to change the world?
Watch a young child for thirty minutes and you’ll see their natural curiosity to solve problems, be creative and communicate. Deep Learning harnesses that natural curiosity and hunger for social connection to design learning environments that pose real problems and opportunities. When learning makes sense, motivation and engagement soar. When students analyse a problem or situation, they are drawn to want to do something about it.
Deep Learning intentionally develops the six competencies so that students have the skills, knowledge and attributes they need to succeed in their lives.

In Deep Learning, we wanted to provide strategies and approaches that foster success for all children
If you had to prioritise educating in three values and three character traits or virtues from the Deep Learning framework, which ones would you choose and why?
The six competencies are not in competition with each other but are an integrated whole. They are all essential, but they’re required with different emphases in different tasks or interactions.
Character and citizenship are crucial in guiding our behaviour. While all six are essential, there is an increasing focus on critical thinking so that students can discern what is real and what is fake in a world of artificial intelligence (AI).
More attention is given to critical thinking so that students can discern what is real and what is fake in an AI world

At a time when artificial intelligence is storming onto the scene at all levels, how is Deep Learning dealing with this new technological revolution?
Technology is now in a position to help us re-imagine learning. Generative AI is showing potential new tools that can change the way the learning process unfolds, but it requires significant discrimination. It should be viewed through the lens of critical thinking with awareness of the global and local impact. As AI takes over some aspects of routine learning, teachers can focus on enriching interactive experiences and collaboration.
In the end, the positive use of AI will depend on the degree of good judgement and discernment of teachers, learners and leaders.